The next objective in the 70-412 path is all about managing roles on failover clusters. This objective will cover adding a role to a failover cluster along with configuring the role properties such as preferred owners, failover settings, and startup priority.
Configuring Roles
- To prepare a service or application for high availability in a failover cluster the service or application needs to be installed on all nodes within the cluster.
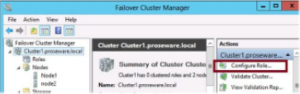
- Then run the High Availability wizard one of the nodes
- Start the wizard by clicking “Configure Role” in the actions pane of the cluster manager
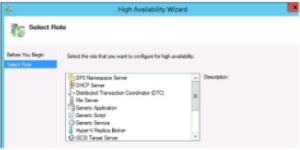
- In the High Availability wizard select the role you want to configure for high availability
- After you select the role, specify a name and IP address that clients will use to connect to the service
- Select the disk on which to store the role data
- Perform any specific configuration steps required for the role
Configuring File Server Role Types
If the File Server role is selected the High Availability wizard prompts you with two choices
- A File Server for General Use
- Stored on normal cluster disks
- Used to support user files stored on file shares
- Scale-Out File Server for Application Data
- Stored on CSVs
- Used to support applications that store data on file shares
- Ensure apps connecting to file shares don’t generate errors during failover
- SoFS clusters not designed for everyday use, they are designed for applications like SQL Server that keep files open on shares for long periods of time, and for highly available virtual machines.
- All nodes in the cluster remain active at once, client requests are distributed among all nodes
Not compatible with Branchcache, Data Deduplication, DFS, DFS Replication, FSRM
Configuring Role Properties
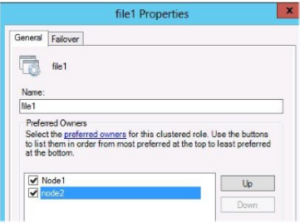
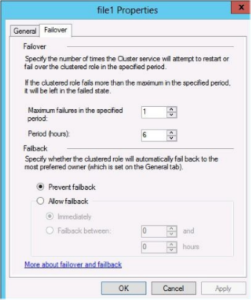
- When the role has been configured for high availability it appears in the centre pane of the Cluster Manager
- At this point you can configure Preferred owner, failover / failback behavior.
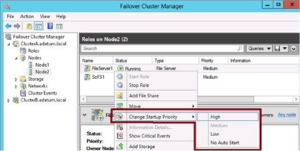
Assigning Role Startup Properties
- 2012 & 201 R2 allow administrators to assign 1 of 4 startup priorities to failover cluster roles
- High
- Medium – default
- Low
- No Auto Start
- When a node fails the priority determines the order in which roles are failed over and started on other nodes
- A higher priority role both fails over and starts before the role of the next highest priority
- No Auto Start – Role is failed over after the other roles but is not started
- Purpose is to ensure all critical roles have prioritized access to resources when they fail
To change the startup priority right click the role in Cluster Manager and select “Change Startup Priority”
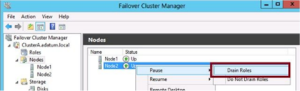
Using Node Drain
- Used to shut down a node for maintenance
- This feature pauses the node and moves all clustered roles over to other nodes, all done in the one action
- Navigate to the nodes container on the Cluster Manager, right click a node, point to pause and select drain roles
- Powershell Suspend-ClusterNode cmdlet
Monitoring Services on Clustered Virtual Machines
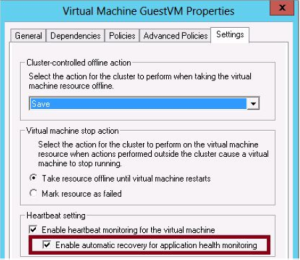
- Windows Server 2012 introduces the ability to monitor the health of services running on clustered VM’s
- If the Hyper-v host determines that a monitored service in a guest VM is in a critical state, the host is able to trigger a recovery
- The Cluster first attempts to recover the VM by restarting it gracefully
- If this fails the cluster service fails the VM over to another node
To monitor VM services with the VM monitoring feature, the following requirements must be met
- Both the Hyper-V host and its guest VM must be running 2012 or 2012 R2
- The guest VM must belong to a domain that trusts the hosts domain
- The failover clustering feature must be installed on the Hyper-V host, the guest VM must also be configured as a role in the failover cluster Hyper-v host
- The administrator connecting to the guest through the failover cluster manager must be a member of the local administrators group on that guest.
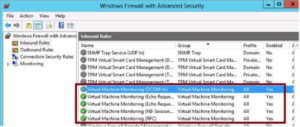
- All F/W rules in the Virtual Machine Monitoring group must be enabled on the guest
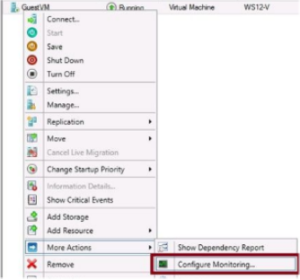
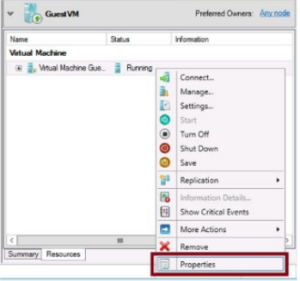
- To configure VM monitoring, right click the VM in failover cluster manager and point to more actions, then select Configure Monitoring
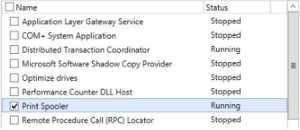
- In the “select services” dialog box that opens, select the service or services you want to monitor
- By default the recovery properties for a service are configured so that it will automatically attempt to restart the first & second time after it fails. After the third failure the cluster service running on the hyper-v host takes over the recovery if you have configured it to do so.
- In some circumstances you may want to redirect the Cluster Service recovery to a third party app that allows more control over the recovery process, in this case disable the default behavior to restart and failover the VM.
So that completes this module, in the next I’ll be looking at Virtual Machine movement, so until next time
Thanks for reading
TSP Admin