ipconfig is a command line utility available in all versions of Windows. Designed to be run from the command prompt, it allows the user to get the IP address information and network configuration from a Windows computer.
Usage
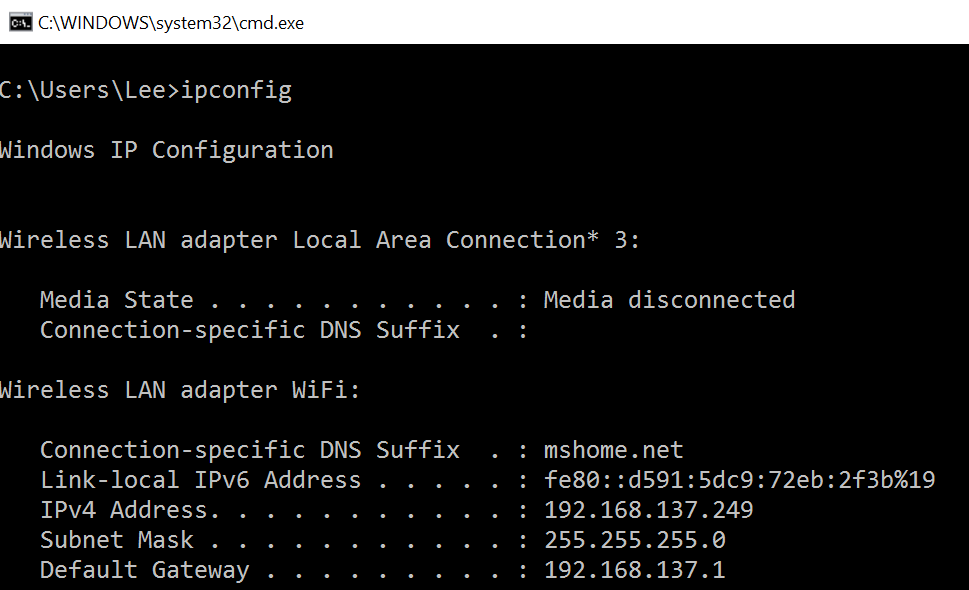
From the command prompt type ipconfig. This will run the utility with the default options and return the IP address, Subnet Mask & Default Gateway for all physical and virtual adapters on the target computer.
ipconfig supports a number of options. To see a complete list of available switches, type ipconfig /?
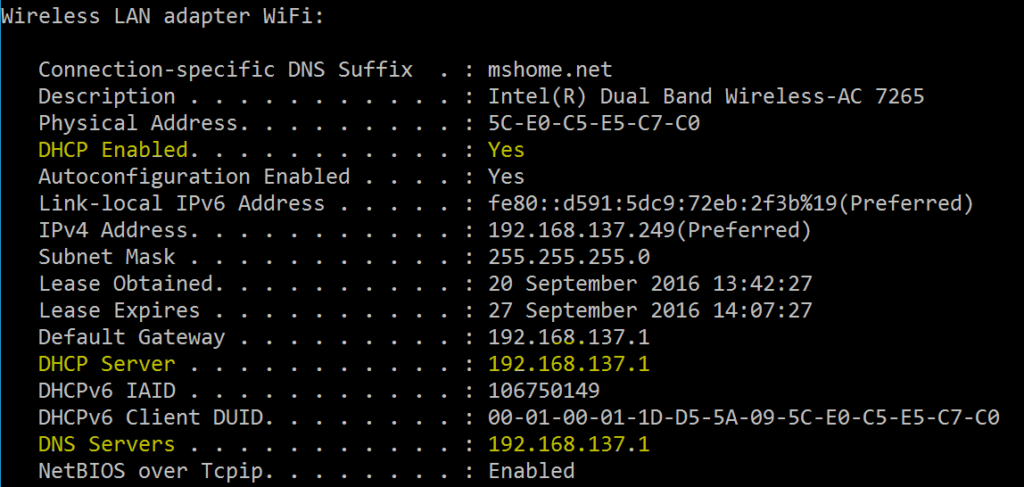
ipconfig /all
This is one of the most useful options, not only does it display the same information as the default option, and additionally displays DNS & DHCP settings for each adapter.
ipconfig /release
The /release option terminates active TCP/IP connections on all network adapters, and releases the ip addresses for use by other applications.
ipconfig /renew
Another extremely useful command, the /renew option establishes TCP/IP connections on all configured network adapters.
Both the renew and the release options only work on clients configured to use DHCP
ipconfig /displayDNS , ipconfig /flushDNS
These options access the contents of the local DNS cache Windows maintains. The DNS cache contains a list of remote computer host names and their corresponding IP addresses. This cache is populated from DNS lookups that occur when attempting to access websites. The /displaydns option displays the contents of the cache, whereas /flushDNS deletes or clears the contents.
ipconfig /registerDNS
This /registerDNS option updates the DNS settings on a Windows computer. Communication is initiated with both the DNS server and the DHCP server to re-register with them.
That concludes my look at ipconfig. A useful tool indeed.
Thanks for reading
TSP Admin