- Rule-Based Management
- Control the security of communications and IT events through rule or filter driven systems.
- Each rule has either an explicit ALLOW or DENY
- Firewall Rules
- First, match the ALLOW rule
- The final rule should always be a default DENY
- VLAN Management
- Hardware imposed network segmentation, created by switches
- Control network traffic for security or performance reasons
- Can also be used to isolate network traffic
- Secure Router Configuration – Prevent malicious or unauthorised route changes
- Configure the administrator password to something unique
- Configure the router to ignore ICMP messages
- Use a secure routing protocol to exchange routing data
- Pre-configure IP addresses of trusted routers
- Configure management interfaces to operate only on the internal network: USE SSH
- ACL (Access Control List)
- Used to define who is allowed or denied permission or access to a resource. Used by Firewalls, Routers, Switches.
- Default DENY
- ALLOW by exceptions
- Port Security
- Physical control of connection points (RJ45 or device ports)
- Can be physical controls or MAC address filtering
- Port Knocking – Ports closed until packets are sent in a specific order
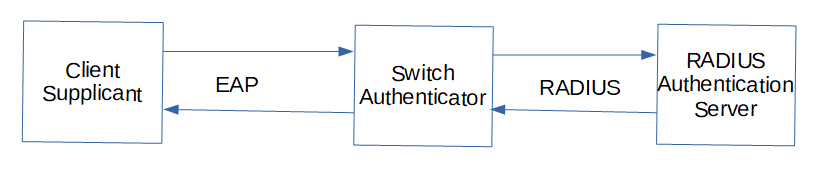
- 802.1X – Port-based authentication mechanism
- Based on the Extensible Authentication Protocol EAP
- Only EAP traffic is allowed until the client authenticates with the RADIUS server
- Flood Guards
- Defence against DDOS attacks. Detects and then auto blocks it
- Loop Protection
- Protection against network loops
- STP – Spanning tree protocol, used in switches
- TTL – Time to live value can also be used
- Network Separation
- More secure
- Use IP subnets and routers if segments need to communicate
- Use firewalls to separate networks that don’t need to communicate
- Log Analysis
- Review audit and sys logs periodically
- Look for evidence of potential policy violations