In this post I will cover the final group of topics in the “Configure File and Storage Solutions” objective domain, Configure and Optimise Storage. The topics are iSCSI, configuring both the target server and initiator, iSNS, what it is and how its used, Features on Demand, Data Deduplication, and finally Storage Tiers which are new to Windows Server 2012 R2.
iSCSI Storage
Windows 2012 & 2012R2 provide both the client and server components for iSCSI, a SAN protocol that carries SCSI commands over IP. Its possible to provide multiple remote servers, shared storage, which is essentially equivalent to directly attached storage.
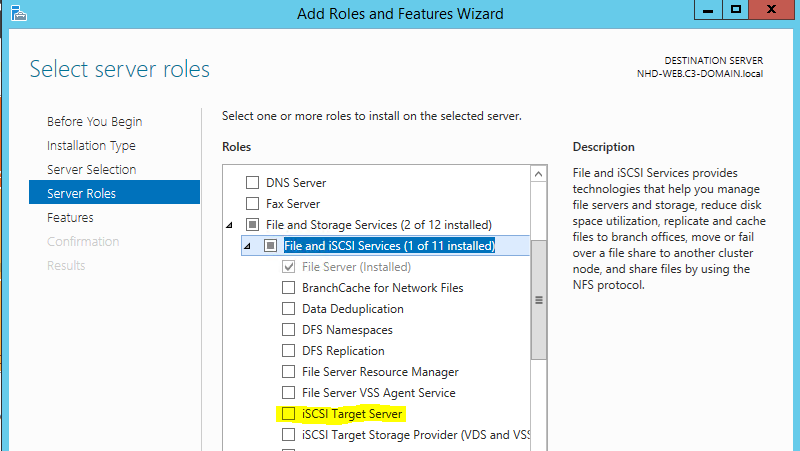
Installing the iSCSI Target Server
The server side of iSCSI storage is called a Target Server. It’s a component of the File and Storage Services Role. This component allows you to create virtual iSCSI disks (VHD files) that can be made to appear as locally attached disks to remote iSCSI clients.
Use PowerShell to install the role: Add-WindowsFeature FS-iSCSTarget-Server
To install the iSCSI Target Server component you have to agree to also install the File Server component.
Enabling the iSCSI Initiator
The iSCSI client component is called the iSCSI Initiator. The initiator is already installed by default, but the associated service (iSCSI initiator service) is not running by default. Start this service and configure it to start automatically.
Understanding iSCSI Components
- iSCSI Target – An iSCSI can include one or more targets. It’s the interface between the set of local iSCSI virtual disks and a defined set of iSCSI initiators
- iSCSI Virtual Disk – A special VHD file that can be added to a iSCSI target
- Logical Unit Number (LUN) – Refers to a logical disk made available through shared storage, a unique value that distinguishes one logical disk from another. Normally assigned automatically by windows
- iSCSI Initiator – A software client that allows the server to use storage found at an iSCSI Target. Before configuring the initiator you first have to configure the target by adding the initiator to the target, then you can configure the initiator to connect to the target.
- iSCSI Qualified Name (IQN) – A network name that initiators and targets use to identify each other.
Configuring iSCSI Storage
To configure iSCSI storage follow these steps, it is assumed that the iSCSI Target Server is already installed on the storage server and the initiator is enabled on the remote server.
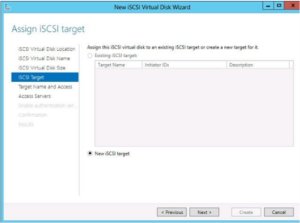
- In server manager on the storage server, create a new iSCSI virtual disk by using the “New Virtual Disk Wizard” – Add this new virtual disk to the target. Once the iSCSI virtual disk has been created assign it to an iSCSI target. If you have not created a target the wizard allows you to create one at this point. To pre-create a iSCSI Target before creating a virtual disk you have to use PowerShell: New-IscsiServerTarget -Targetname “Target1”
Configure the initiator on the remote server to connect to the iSCSI target
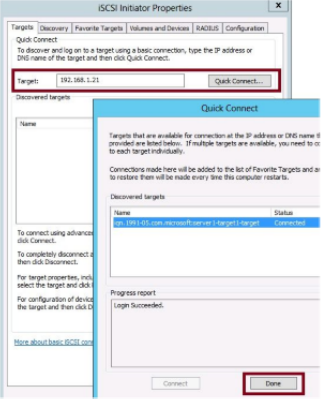
- When the virtual disk and iSCSI target have been created and the target configured with an initiator, its time to configure that initiator to point to the same target. This is done using the iSCSI Initiator tool.
- In the initiator tool on the remote server type in the IP address of the target server the click quick connect.
- If the initiator has been added to the target, the target should be discovered, identified by its IQN. Click done and click ok to approve the target.
- When the new disks appear on the remote server in server manager, bring them on line and initialize them, and create volumes as needed. Only after the new volume is created can the new storage appear as a drive letter in Windows explorer.
Managing Existing iSCSI Virtual Disks and Targets
Use Service Manager on the Target server to modify iSCSI virtual disks that have already been created. You are able too
- Assign or re-assign a virtual disk to target

- Extend the disk
- Disable the disk
- Remove the disk from the target
- Properties allows modification of the LUN value
Using Internet iStorage Name Service (iSNS) Server
iSNS is an installable Windows Server feature. It acts as a central repository of iSCSI components that are available on the network. iSNS works as follows
- First register the iSCSI initiators & targets with the iSNS server
- Configure each initiator with the IP address of the iSNS server
- Initiators are now able to query iSNS for a list of available targets on the network
Using Features On Demand
A copy of all the binary files for all features and roles installed during windows setup are stored in a directory called the side-by-side store located in Windows\WinSxS
Keeping this copy takes up space but does allow admins to install any feature or roles without needing access to media.
In 2012 & 2012 R2 its possible to delete the files for features not being used from the side-by-side store. This ability is called Features on Demand, and can reduce the installation footprint of the installation.
To later reinstall a role or feature for which files have been deleted you need access to the 2012 source files.
To completely remove all files or a role or feature from disk use the Uninstall-WindowsFeature cmdlet and specify the name of the feature using the –Remove parameter.
Installing the Data Deduplication Component
Data Deduplication is a installable component of the File and Storage Services role. Allows windows you to reduce redundant (duplicate) chunks of data saved in storage.
Installed as part of the File and Storage Service module
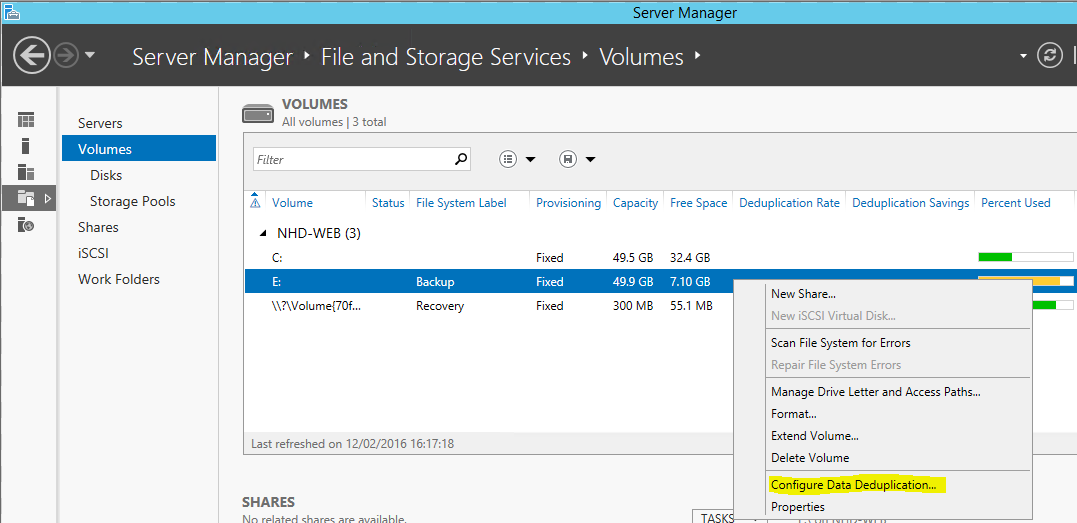
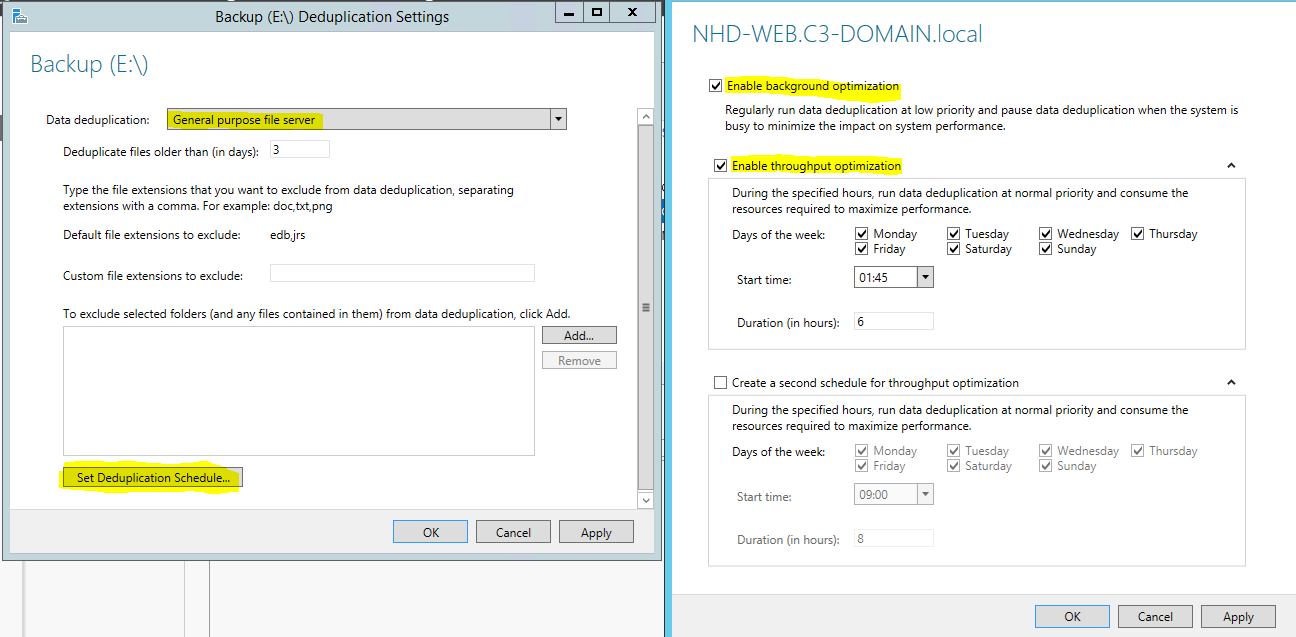
Configured through the File & Storage Services page on Server Manager, right click any volume and select “Configure Data Deduplication”
- Enable Data Deduplication of the volume
- Set minimum age for files targeted, and exclude any files from the process
- Set a deduplication schedule, the process runs in the background scanning files. Default option is to “Enable Background Optimization”, runs with no defined schedule but runs frequently as a low priority task.
- Possible to evaluate the space savings without enabling data deduplication by using the Deduplication Data Evaluation Tool (DDPEval.exe)
Using Storage Tiers
Storage tiers allow you to create virtual disks that are made up of both SSDs and HDD. Storage tier functionality automatically moves data based on how frequently its accessed. Frequently access data is moved to the part of the VHD stored on the SSDs, while less frequently accessed data is stored on the HDDs. By using storage tiers you get most of the performance advantages of using SSD without requiring all the storage to be made from SSDs.
Typical configuration involves having 4 SSDs and 8 HDDs
Data is moved between standard and fast tiers depending on how often its accessed, you can also Pin files to either tier using the Set-FileStorageTier PowerShell cmdlet
- Only supported on 2012 R2
- When creating a storage space with tiers the VHD must use fixed provisioning
- Number of columns must be identical, (a two column two way mirror with storage tiers required four SSDs and 4 HDD)
- Ensure that volumes created on storage tier VHD are the same size as the virtual disk.
So that concludes the second objective domain, for the 70-412 exam. Some really interesting subjects are covered here and I really enjoyed reviewing my study notes again to create these posts.
Thanks for reading and remember, keep those computers up to date.
TSP Admin